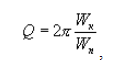-
1 maximum regime
дв. максимальный режимEnglsh-Russian aviation and space dictionary > maximum regime
-
2 regime
-
3 maximum rating
максимальная нагрузка
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
максимальный режим работы ГТД
максимальный режим
Установившийся режим работы ГТД, характеризуемый максимальной тягой (мощностью) на земле или в полете в течение ограниченного времени.
Примечание
Параметры ГТД на максимальном режиме имеют индекс «mах».
[ ГОСТ 23851-79]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > maximum rating
-
4 maximum continuons rating
максимальный продолжительный режим работы ГТД
максимальный продолжительный режим
Установившийся режим работы ГТД, характеризуемый пониженными по сравнению с максимальным режимом значениями частоты вращения ротора (роторов) и температуры газа перед турбиной, при которых двигатель может работать с ограниченной по времени общей наработкой.
Примечания
1. Параметры ГТД на максимальном продолжительном режиме имеют индекс «mах пр».
2. Для некоторых ГТД частота вращения ротора может оставаться неизменной.
[ ГОСТ 23851-79]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > maximum continuons rating
-
5 augmented turbojet (turfofan) maximum afterburning rating
полный форсированный режим работы ТРДФ (ТРДДФ)
полный форсированный режим
Ндп. полный форсажный режим работы ТРДФ (ТРДДФ)
Форсированный режим работы ТРДФ (ТРДДФ), характеризуемый максимальным расходом топлива в форсажной камере сгорания при максимальных частоте вращения ротора (роторов), двигателя и температуре газа перед турбиной.
Примечание
Параметры ГТД на полном форсированном режиме имеют индекс «ПФ».
[ ГОСТ 23851-79]Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Тематики
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
250. Полный форсированный режим работы ТРДФ (ТРДДФ)
Полный форсированный режим
Ндп. Полный форсажный режим работы ТРДФ ( ТРДДФ)
D. Betriebszustand mit maximaler Nachverbrennung
E. Augmented turbojet (turfofan) maximum afterburning rating
F. Régime de fonctionnement du TRPC (TRDFPC) á pleine réchauffe
Форсированный режим работы ТРДФ (ТРДДФ), характеризуемый максимальным расходом топлива в форсажной камере сгорания при максимальных частоте вращения ротора (роторов), двигателя и температуре газа перед турбиной.
Примечание. Параметры ГТД на полном форсированном режиме имеют индекс «ПФ».
Источник: ГОСТ 23851-79: Двигатели газотурбинные авиационные. Термины и определения оригинал документа
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > augmented turbojet (turfofan) maximum afterburning rating
-
6 available capacity of a power station
располагаемая мощность агрегата (электростанции)
Установленная мощность генерирующего агрегата (электростанции), за вычетом ограничений его мощности.
[ ГОСТ 19431-84]EN
available capacity of a unit
the maximum power at which a unit can be operated continuously under the prevailing conditions
Note – This power may be gross or net.
[IEV ref 602-03-11]
available capacity of a power station
the maximum power at which a power station can be operated continuously under the prevailing conditions
Note – This power may be gross or net.
[IEV ref 602-03-12]FR
puissance disponible d'une tranche
puissance maximale réalisable en régime continu dans les conditions réelles où une tranche se trouve
Note – Cette puissance peut être brute ou nette.
[IEV ref 602-03-11]
puissance disponible d'une centrale
puissance maximale réalisable en régime continu dans les conditions réelles où une centrale se trouve
Note – Cette puissance peut être brute ou nette.
[IEV ref 602-03-12]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
DE
- verfügbare Leistung eines Blocks, f
- verfügbare Leistung eines Kraftwerks
FR
- puissance disponible d'une centrale
- puissance disponible d'une tranche
- puissance disponible d’une centrale
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > available capacity of a power station
-
7 available capacity of a unit
располагаемая мощность агрегата (электростанции)
Установленная мощность генерирующего агрегата (электростанции), за вычетом ограничений его мощности.
[ ГОСТ 19431-84]EN
available capacity of a unit
the maximum power at which a unit can be operated continuously under the prevailing conditions
Note – This power may be gross or net.
[IEV ref 602-03-11]
available capacity of a power station
the maximum power at which a power station can be operated continuously under the prevailing conditions
Note – This power may be gross or net.
[IEV ref 602-03-12]FR
puissance disponible d'une tranche
puissance maximale réalisable en régime continu dans les conditions réelles où une tranche se trouve
Note – Cette puissance peut être brute ou nette.
[IEV ref 602-03-11]
puissance disponible d'une centrale
puissance maximale réalisable en régime continu dans les conditions réelles où une centrale se trouve
Note – Cette puissance peut être brute ou nette.
[IEV ref 602-03-12]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
DE
- verfügbare Leistung eines Blocks, f
- verfügbare Leistung eines Kraftwerks
FR
- puissance disponible d'une centrale
- puissance disponible d'une tranche
- puissance disponible d’une centrale
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > available capacity of a unit
-
8 available power station capacity
располагаемая мощность агрегата (электростанции)
Установленная мощность генерирующего агрегата (электростанции), за вычетом ограничений его мощности.
[ ГОСТ 19431-84]EN
available capacity of a unit
the maximum power at which a unit can be operated continuously under the prevailing conditions
Note – This power may be gross or net.
[IEV ref 602-03-11]
available capacity of a power station
the maximum power at which a power station can be operated continuously under the prevailing conditions
Note – This power may be gross or net.
[IEV ref 602-03-12]FR
puissance disponible d'une tranche
puissance maximale réalisable en régime continu dans les conditions réelles où une tranche se trouve
Note – Cette puissance peut être brute ou nette.
[IEV ref 602-03-11]
puissance disponible d'une centrale
puissance maximale réalisable en régime continu dans les conditions réelles où une centrale se trouve
Note – Cette puissance peut être brute ou nette.
[IEV ref 602-03-12]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
DE
- verfügbare Leistung eines Blocks, f
- verfügbare Leistung eines Kraftwerks
FR
- puissance disponible d'une centrale
- puissance disponible d'une tranche
- puissance disponible d’une centrale
52. Располагаемая мощность агрегата (электростанции)
Располагаемая мощность
E. Available power station capacity
F. Puissance disponible d’une centrale
Установленная мощность генерирующего агрегата (электростанции), за вычетом ограничений его мощности
Источник: ГОСТ 19431-84: Энергетика и электрификация. Термины и определения оригинал документа
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > available power station capacity
-
9 continuous current-carrying capacity
длительная пропускная способность по току
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > continuous current-carrying capacity
-
10 ampacity (US)
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > ampacity (US)
-
11 continuous current
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
непрерывный ток
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > continuous current
-
12 current-carrying capacity
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
предельно допустимый ток
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
прочность печатной платы к токовой нагрузке
Свойство печатной платы сохранять электрические и механические характеристики после воздействия максимально допустимой токовой нагрузки на печатный проводник или металлизированное отверстие печатной платы.
[ ГОСТ Р 53386-2009]Тематики
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > current-carrying capacity
-
13 cyclic rating factor
коэффициент циклической токовой нагрузки (кабелей)
Коэффициент, на который может быть умножен номинальный ток установившегося режима, соответствующий коэффициенту нагрузки 100 %, для получения допустимого пикового значения тока в течение суточного цикла, при котором температура токопроводящей жилы в течение этого цикла достигает, но не превышает максимально допустимое значение
[IEV number 461-23-02]EN
cyclic rating factor
factor by which the permissible steady-state rated current corresponding to a 100 % load factor may be multiplied to obtain the permissible peak value of current during a daily cycle such that the conductor attains, but does not exceed, the maximum rated temperature during the cycle
[IEV number 461-23-02]FR
facteur de régime cyclique
facteur par lequel le courant assigné admissible en régime permanent, correspondant à un facteur de charge 100 %, peut être multiplié pour obtenir la valeur de pointe du courant au cours d'un cycle journalier, de sorte qu'au cours de ce cycle, l'âme atteigne sans la dépasser la température assignée maximale
[IEV number 461-23-02]Тематики
- кабели, провода...
EN
DE
FR
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > cyclic rating factor
-
14 theory
1) теория•-
Abbe's theory
-
Abbe theory
-
absolute reaction rate theory
-
acid-basic catalysis theory
-
adhesive theory of friction
-
affinity theory
-
age theory
-
Airy-Stokes theory
-
approximation theory
-
Arrhenius theory
-
association theory
-
automata theory
-
automatic control theory
-
behavior theory of canals
-
boundary-layer interaction theory
-
boundary-layer theory
-
Bronsted theory
-
bunching theory
-
catastrophe theory
-
chemical graph theory
-
chemical kinetics theory
-
circuit theory
-
coding theory
-
combinatorial theory
-
communications theory
-
communication theory
-
constant angle theory of arch dam design
-
contact clastohydrodynamic theory
-
control theory
-
control-system theory
-
coordination theory
-
Coulomb's wedge theory
-
cylinder theory of arch dam design
-
delamination theory of wear
-
diffraction theory
-
diffusion theory
-
dispersion theory
-
dissociation theory
-
donor-acceptor interaction theory
-
double shear theory
-
drag theory
-
effective arch theory
-
elastic theory
-
elastic wave theory
-
elasticity theory
-
electromagnetic field theory
-
electromagnetic theory
-
energetical wear theory
-
erosion theory
-
estimation theory
-
evaporation theory
-
fatigue theory of wear
-
fatigue theory
-
field theory
-
filter theory
-
flash temperature theory
-
Flory theory
-
free space theory
-
free volume theory
-
free-electron theory of metals
-
fuzzy-set theory
-
game theory
-
general theory
-
generalized electric machine theory
-
graph theory
-
gravitational theory
-
gravitation theory
-
group theory
-
handling theory
-
hydroxo-complex theory
-
imperfection theory
-
information theory
-
ionic theory
-
kinetic theory of gases
-
kinetic theory of liquids
-
local theory
-
logic theory
-
long-range stress theory
-
magnetic field theory
-
magnetotelluric theory
-
mapping theory
-
mathematical economic theory
-
maximum shear theory
-
maximum strain energy theory
-
Maxwell's electromagnetic theory
-
mechanical interlocking friction theory
-
membrane theory
-
mixing length theory
-
model theory
-
molecular attraction friction theory
-
molecular theory
-
molecular-kinetic theory
-
molecular-mechanical theory of friction
-
mosaic-block theory
-
multienergy-group diffusion theory
-
multigroup theory
-
multiple catalysis theory
-
multiple seismometer theory
-
network flow theory
-
network theory
-
nuclear drop theory
-
nuclear theory
-
number theory
-
nutrient theory
-
one-speed diffusion theory
-
oxidational theory of wear
-
oxide-film barrier theory
-
oxyacid theory
-
oxygen attack theory
-
peracid theory of gum formation
-
perturbation theory
-
plastic collapse theory
-
plastic theory
-
plasticity theory
-
plate theory
-
potential field theory
-
potential theory
-
prediction theory
-
probability theory
-
quantum field theory
-
quantum theory of light
-
queueing theory
-
queuing theory
-
radiometry theory
-
Rankine's theory
-
ray-path theory
-
ray theory
-
reflection theory
-
refraction theory
-
regime theory of rivers
-
renewal theory
-
scaled-particle theory
-
seismic theory
-
set theory
-
solid-state theory
-
solvation theory
-
stability theory
-
statistical-decision theory
-
steady-state creep theory
-
superlattice theory
-
system theory
-
theory of algorithms
-
theory of chances
-
theory of elasticity
-
theory of errors
-
theory of failure
-
theory of functions
-
theory of lateral earth pressure
-
theory of limits
-
theory of magnetism
-
theory of oscillations
-
theory of plasticity
-
theory of reliability
-
theory of scheduling
-
theory of screws
-
theory of similarity
-
theory of specific heats
-
theory of stream lines
-
theory of strength
-
theory of testing
-
theory of thermoelastic instability of contact
-
theory of vibrations
-
thermodiffusion theory
-
thermofluctuational strength theory
-
tidal-wave theory
-
tractive-force theory
-
transition state theory
-
transport theory
-
unified electrical machine theory
-
utility theory
-
valence bond theory
-
valency theory
-
variable-radius theory
-
wave theory of light
-
welding-shearing friction theory
-
zone theory of solids -
15 near cash
!гос. фин. The resource budget contains a separate control total for “near cash” expenditure, that is expenditure such as pay and current grants which impacts directly on the measure of the golden rule.This paper provides background information on the framework for the planning and control of public expenditure in the UK which has been operated since the 1998 Comprehensive Spending Review (CSR). It sets out the different classifications of spending for budgeting purposes and why these distinctions have been adopted. It discusses how the public expenditure framework is designed to ensure both sound public finances and an outcome-focused approach to public expenditure.The UK's public spending framework is based on several key principles:"consistency with a long-term, prudent and transparent regime for managing the public finances as a whole;" "the judgement of success by policy outcomes rather than resource inputs;" "strong incentives for departments and their partners in service delivery to plan over several years and plan together where appropriate so as to deliver better public services with greater cost effectiveness; and"the proper costing and management of capital assets to provide the right incentives for public investment.The Government sets policy to meet two firm fiscal rules:"the Golden Rule states that over the economic cycle, the Government will borrow only to invest and not to fund current spending; and"the Sustainable Investment Rule states that net public debt as a proportion of GDP will be held over the economic cycle at a stable and prudent level. Other things being equal, net debt will be maintained below 40 per cent of GDP over the economic cycle.Achievement of the fiscal rules is assessed by reference to the national accounts, which are produced by the Office for National Statistics, acting as an independent agency. The Government sets its spending envelope to comply with these fiscal rules.Departmental Expenditure Limits ( DEL) and Annually Managed Expenditure (AME)"Departmental Expenditure Limit ( DEL) spending, which is planned and controlled on a three year basis in Spending Reviews; and"Annually Managed Expenditure ( AME), which is expenditure which cannot reasonably be subject to firm, multi-year limits in the same way as DEL. AME includes social security benefits, local authority self-financed expenditure, debt interest, and payments to EU institutions.More information about DEL and AME is set out below.In Spending Reviews, firm DEL plans are set for departments for three years. To ensure consistency with the Government's fiscal rules departments are set separate resource (current) and capital budgets. The resource budget contains a separate control total for “near cash” expenditure, that is expenditure such as pay and current grants which impacts directly on the measure of the golden rule.To encourage departments to plan over the medium term departments may carry forward unspent DEL provision from one year into the next and, subject to the normal tests for tautness and realism of plans, may be drawn down in future years. This end-year flexibility also removes any incentive for departments to use up their provision as the year end approaches with less regard to value for money. For the full benefits of this flexibility and of three year plans to feed through into improved public service delivery, end-year flexibility and three year budgets should be cascaded from departments to executive agencies and other budget holders.Three year budgets and end-year flexibility give those managing public services the stability to plan their operations on a sensible time scale. Further, the system means that departments cannot seek to bid up funds each year (before 1997, three year plans were set and reviewed in annual Public Expenditure Surveys). So the credibility of medium-term plans has been enhanced at both central and departmental level.Departments have certainty over the budgetary allocation over the medium term and these multi-year DEL plans are strictly enforced. Departments are expected to prioritise competing pressures and fund these within their overall annual limits, as set in Spending Reviews. So the DEL system provides a strong incentive to control costs and maximise value for money.There is a small centrally held DEL Reserve. Support from the Reserve is available only for genuinely unforeseeable contingencies which departments cannot be expected to manage within their DEL.AME typically consists of programmes which are large, volatile and demand-led, and which therefore cannot reasonably be subject to firm multi-year limits. The biggest single element is social security spending. Other items include tax credits, Local Authority Self Financed Expenditure, Scottish Executive spending financed by non-domestic rates, and spending financed from the proceeds of the National Lottery.AME is reviewed twice a year as part of the Budget and Pre-Budget Report process reflecting the close integration of the tax and benefit system, which was enhanced by the introduction of tax credits.AME is not subject to the same three year expenditure limits as DEL, but is still part of the overall envelope for public expenditure. Affordability is taken into account when policy decisions affecting AME are made. The Government has committed itself not to take policy measures which are likely to have the effect of increasing social security or other elements of AME without taking steps to ensure that the effects of those decisions can be accommodated prudently within the Government's fiscal rules.Given an overall envelope for public spending, forecasts of AME affect the level of resources available for DEL spending. Cautious estimates and the AME margin are built in to these AME forecasts and reduce the risk of overspending on AME.Together, DEL plus AME sum to Total Managed Expenditure (TME). TME is a measure drawn from national accounts. It represents the current and capital spending of the public sector. The public sector is made up of central government, local government and public corporations.Resource and Capital Budgets are set in terms of accruals information. Accruals information measures resources as they are consumed rather than when the cash is paid. So for example the Resource Budget includes a charge for depreciation, a measure of the consumption or wearing out of capital assets."Non cash charges in budgets do not impact directly on the fiscal framework. That may be because the national accounts use a different way of measuring the same thing, for example in the case of the depreciation of departmental assets. Or it may be that the national accounts measure something different: for example, resource budgets include a cost of capital charge reflecting the opportunity cost of holding capital; the national accounts include debt interest."Within the Resource Budget DEL, departments have separate controls on:"Near cash spending, the sub set of Resource Budgets which impacts directly on the Golden Rule; and"The amount of their Resource Budget DEL that departments may spend on running themselves (e.g. paying most civil servants’ salaries) is limited by Administration Budgets, which are set in Spending Reviews. Administration Budgets are used to ensure that as much money as practicable is available for front line services and programmes. These budgets also help to drive efficiency improvements in departments’ own activities. Administration Budgets exclude the costs of frontline services delivered directly by departments.The Budget preceding a Spending Review sets an overall envelope for public spending that is consistent with the fiscal rules for the period covered by the Spending Review. In the Spending Review, the Budget AME forecast for year one of the Spending Review period is updated, and AME forecasts are made for the later years of the Spending Review period.The 1998 Comprehensive Spending Review ( CSR), which was published in July 1998, was a comprehensive review of departmental aims and objectives alongside a zero-based analysis of each spending programme to determine the best way of delivering the Government's objectives. The 1998 CSR allocated substantial additional resources to the Government's key priorities, particularly education and health, for the three year period from 1999-2000 to 2001-02.Delivering better public services does not just depend on how much money the Government spends, but also on how well it spends it. Therefore the 1998 CSR introduced Public Service Agreements (PSAs). Each major government department was given its own PSA setting out clear targets for achievements in terms of public service improvements.The 1998 CSR also introduced the DEL/ AME framework for the control of public spending, and made other framework changes. Building on the investment and reforms delivered by the 1998 CSR, successive spending reviews in 2000, 2002 and 2004 have:"provided significant increase in resources for the Government’s priorities, in particular health and education, and cross-cutting themes such as raising productivity; extending opportunity; and building strong and secure communities;" "enabled the Government significantly to increase investment in public assets and address the legacy of under investment from past decades. Departmental Investment Strategies were introduced in SR2000. As a result there has been a steady increase in public sector net investment from less than ¾ of a per cent of GDP in 1997-98 to 2¼ per cent of GDP in 2005-06, providing better infrastructure across public services;" "introduced further refinements to the performance management framework. PSA targets have been reduced in number over successive spending reviews from around 300 to 110 to give greater focus to the Government’s highest priorities. The targets have become increasingly outcome-focused to deliver further improvements in key areas of public service delivery across Government. They have also been refined in line with the conclusions of the Devolving Decision Making Review to provide a framework which encourages greater devolution and local flexibility. Technical Notes were introduced in SR2000 explaining how performance against each PSA target will be measured; and"not only allocated near cash spending to departments, but also – since SR2002 - set Resource DEL plans for non cash spending.To identify what further investments and reforms are needed to equip the UK for the global challenges of the decade ahead, on 19 July 2005 the Chief Secretary to the Treasury announced that the Government intends to launch a second Comprehensive Spending Review (CSR) reporting in 2007.A decade on from the first CSR, the 2007 CSR will represent a long-term and fundamental review of government expenditure. It will cover departmental allocations for 2008-09, 2009-10 and 2010 11. Allocations for 2007-08 will be held to the agreed figures already announced by the 2004 Spending Review. To provide a rigorous analytical framework for these departmental allocations, the Government will be taking forward a programme of preparatory work over 2006 involving:"an assessment of what the sustained increases in spending and reforms to public service delivery have achieved since the first CSR. The assessment will inform the setting of new objectives for the decade ahead;" "an examination of the key long-term trends and challenges that will shape the next decade – including demographic and socio-economic change, globalisation, climate and environmental change, global insecurity and technological change – together with an assessment of how public services will need to respond;" "to release the resources needed to address these challenges, and to continue to secure maximum value for money from public spending over the CSR period, a set of zero-based reviews of departments’ baseline expenditure to assess its effectiveness in delivering the Government’s long-term objectives; together with"further development of the efficiency programme, building on the cross cutting areas identified in the Gershon Review, to embed and extend ongoing efficiency savings into departmental expenditure planning.The 2007 CSR also offers the opportunity to continue to refine the PSA framework so that it drives effective delivery and the attainment of ambitious national standards.Public Service Agreements (PSAs) were introduced in the 1998 CSR. They set out agreed targets detailing the outputs and outcomes departments are expected to deliver with the resources allocated to them. The new spending regime places a strong emphasis on outcome targets, for example in providing for better health and higher educational standards or service standards. The introduction in SR2004 of PSA ‘standards’ will ensure that high standards in priority areas are maintained.The Government monitors progress against PSA targets, and departments report in detail twice a year in their annual Departmental Reports (published in spring) and in their autumn performance reports. These reports provide Parliament and the public with regular updates on departments’ performance against their targets.Technical Notes explain how performance against each PSA target will be measured.To make the most of both new investment and existing assets, there needs to be a coherent long term strategy against which investment decisions are taken. Departmental Investment Strategies (DIS) set out each department's plans to deliver the scale and quality of capital stock needed to underpin its objectives. The DIS includes information about the department's existing capital stock and future plans for that stock, as well as plans for new investment. It also sets out the systems that the department has in place to ensure that it delivers its capital programmes effectively.This document was updated on 19 December 2005.Near-cash resource expenditure that has a related cash implication, even though the timing of the cash payment may be slightly different. For example, expenditure on gas or electricity supply is incurred as the fuel is used, though the cash payment might be made in arrears on aquarterly basis. Other examples of near-cash expenditure are: pay, rental.Net cash requirement the upper limit agreed by Parliament on the cash which a department may draw from theConsolidated Fund to finance the expenditure within the ambit of its Request forResources. It is equal to the agreed amount of net resources and net capital less non-cashitems and working capital.Non-cash cost costs where there is no cash transaction but which are included in a body’s accounts (or taken into account in charging for a service) to establish the true cost of all the resourcesused.Non-departmental a body which has a role in the processes of government, but is not a government public body, NDPBdepartment or part of one. NDPBs accordingly operate at arm’s length from governmentMinisters.Notional cost of a cost which is taken into account in setting fees and charges to improve comparability with insuranceprivate sector service providers.The charge takes account of the fact that public bodies donot generally pay an insurance premium to a commercial insurer.the independent body responsible for collecting and publishing official statistics about theUK’s society and economy. (At the time of going to print legislation was progressing tochange this body to the Statistics Board).Office of Government an office of the Treasury, with a status similar to that of an agency, which aims to maximise Commerce, OGCthe government’s purchasing power for routine items and combine professional expertiseto bear on capital projects.Office of the the government department responsible for discharging the Paymaster General’s statutoryPaymaster General,responsibilities to hold accounts and make payments for government departments and OPGother public bodies.Orange bookthe informal title for Management of Risks: Principles and Concepts, which is published by theTreasury for the guidance of public sector bodies.Office for NationalStatistics, ONS60Managing Public Money————————————————————————————————————————"GLOSSARYOverdraftan account with a negative balance.Parliament’s formal agreement to authorise an activity or expenditure.Prerogative powerspowers exercisable under the Royal Prerogative, ie powers which are unique to the Crown,as contrasted with common-law powers which may be available to the Crown on the samebasis as to natural persons.Primary legislationActs which have been passed by the Westminster Parliament and, where they haveappropriate powers, the Scottish Parliament and the Northern Ireland Assembly. Begin asBills until they have received Royal Assent.arrangements under which a public sector organisation contracts with a private sectorentity to construct a facility and provide associated services of a specified quality over asustained period. See annex 7.5.Proprietythe principle that patterns of resource consumption should respect Parliament’s intentions,conventions and control procedures, including any laid down by the PAC. See box 2.4.Public Accountssee Committee of Public Accounts.CommitteePublic corporationa trading body controlled by central government, local authority or other publiccorporation that has substantial day to day operating independence. See section 7.8.Public Dividend finance provided by government to public sector bodies as an equity stake; an alternative to Capital, PDCloan finance.Public Service sets out what the public can expect the government to deliver with its resources. EveryAgreement, PSAlarge government department has PSA(s) which specify deliverables as targets or aimsrelated to objectives.a structured arrangement between a public sector and a private sector organisation tosecure an outcome delivering good value for money for the public sector. It is classified tothe public or private sector according to which has more control.Rate of returnthe financial remuneration delivered by a particular project or enterprise, expressed as apercentage of the net assets employed.Regularitythe principle that resource consumption should accord with the relevant legislation, therelevant delegated authority and this document. See box 2.4.Request for the functional level into which departmental Estimates may be split. RfRs contain a number Resources, RfRof functions being carried out by the department in pursuit of one or more of thatdepartment’s objectives.Resource accountan accruals account produced in line with the Financial Reporting Manual (FReM).Resource accountingthe system under which budgets, Estimates and accounts are constructed in a similar wayto commercial audited accounts, so that both plans and records of expenditure allow in fullfor the goods and services which are to be, or have been, consumed – ie not just the cashexpended.Resource budgetthe means by which the government plans and controls the expenditure of resources tomeet its objectives.Restitutiona legal concept which allows money and property to be returned to its rightful owner. Ittypically operates where another person can be said to have been unjustly enriched byreceiving such monies.Return on capital the ratio of profit to capital employed of an accounting entity during an identified period.employed, ROCEVarious measures of profit and of capital employed may be used in calculating the ratio.Public Privatepartnership, PPPPrivate Finance Initiative, PFIParliamentaryauthority61Managing Public Money"————————————————————————————————————————GLOSSARYRoyal charterthe document setting out the powers and constitution of a corporation established underprerogative power of the monarch acting on Privy Council advice.Second readingthe second formal time that a House of Parliament may debate a bill, although in practicethe first substantive debate on its content. If successful, it is deemed to denoteParliamentary approval of the principle of the proposed legislation.Secondary legislationlaws, including orders and regulations, which are made using powers in primary legislation.Normally used to set out technical and administrative provision in greater detail thanprimary legislation, they are subject to a less intense level of scrutiny in Parliament.European legislation is,however,often implemented in secondary legislation using powers inthe European Communities Act 1972.Service-level agreement between parties, setting out in detail the level of service to be performed.agreementWhere agreements are between central government bodies, they are not legally a contractbut have a similar function.Shareholder Executive a body created to improve the government’s performance as a shareholder in businesses.Spending reviewsets out the key improvements in public services that the public can expect over a givenperiod. It includes a thorough review of departmental aims and objectives to find the bestway of delivering the government’s objectives, and sets out the spending plans for the givenperiod.State aidstate support for a domestic body or company which could distort EU competition and sois not usually allowed. See annex 4.9.Statement of Excessa formal statement detailing departments’ overspends prepared by the Comptroller andAuditor General as a result of undertaking annual audits.Statement on Internal an annual statement that Accounting Officers are required to make as part of the accounts Control, SICon a range of risk and control issues.Subheadindividual elements of departmental expenditure identifiable in Estimates as single cells, forexample cell A1 being administration costs within a particular line of departmental spending.Supplyresources voted by Parliament in response to Estimates, for expenditure by governmentdepartments.Supply Estimatesa statement of the resources the government needs in the coming financial year, and forwhat purpose(s), by which Parliamentary authority is sought for the planned level ofexpenditure and income.Target rate of returnthe rate of return required of a project or enterprise over a given period, usually at least a year.Third sectorprivate sector bodies which do not act commercially,including charities,social and voluntaryorganisations and other not-for-profit collectives. See annex 7.7.Total Managed a Treasury budgeting term which covers all current and capital spending carried out by the Expenditure,TMEpublic sector (ie not just by central departments).Trading fundan organisation (either within a government department or forming one) which is largely orwholly financed from commercial revenue generated by its activities. Its Estimate shows itsnet impact, allowing its income from receipts to be devoted entirely to its business.Treasury Minutea formal administrative document drawn up by the Treasury, which may serve a wide varietyof purposes including seeking Parliamentary approval for the use of receipts asappropriations in aid, a remission of some or all of the principal of voted loans, andresponding on behalf of the government to reports by the Public Accounts Committee(PAC).62Managing Public Money————————————————————————————————————————GLOSSARY63Managing Public MoneyValue for moneythe process under which organisation’s procurement, projects and processes aresystematically evaluated and assessed to provide confidence about suitability, effectiveness,prudence,quality,value and avoidance of error and other waste,judged for the public sectoras a whole.Virementthe process through which funds are moved between subheads such that additionalexpenditure on one is met by savings on one or more others.Votethe process by which Parliament approves funds in response to supply Estimates.Voted expenditureprovision for expenditure that has been authorised by Parliament. Parliament ‘votes’authority for public expenditure through the Supply Estimates process. Most expenditureby central government departments is authorised in this way.Wider market activity activities undertaken by central government organisations outside their statutory duties,using spare capacity and aimed at generating a commercial profit. See annex 7.6.Windfallmonies received by a department which were not anticipated in the spending review.———————————————————————————————————————— -
16 phraseology of meteorological breefing/consultation
фразеология метеоконсультацииThis is the 0600 UTC surface synoptic (significant weather, high level) chart.
– Это приземная синоптическая (особых явлений, высотная) карта за 0600 UTC.This prognostic significant weather (high level, 200, 300 hPa) chart is valid for 1800 UTC.
– Эта прогностическая карта особых явлений (высотная, 200, 300 гПа) на 18 UTC.Wind speed and displacement of baric systems on our charts is given in kmh.
– Скорость ветра и смещения барических систем на наших картах указана в км/ч.Altitudes on our charts are given in decametres.
– Высоты на наших картах даны в декаметрах.This cyclone (anticyclone) according to data of barric topography is tracked up to the altitude of... km.
– Этот циклон (антициклон) по данным барической топографии прослеживается до высоты... км.The cyclone (anticyclone) centred at (Northern, Southern...) Norway is displacing North-East (South...) with the speed of... kmh.
– Циклон (антициклон), расположенный над (северной, южной...) Норвегией смещается к северо-востоку (югу...) со скоростью... км/ч.The low (high) centred North (South...) of the Bahames is moving North-Eastward (South-Eastward...) at about 20 kmh and is deepening.
– Циклон (антициклон), расположенный севернее (южнее...) Багамских о-вов, смещается в северо-восточном (юго-восточном...) направлении со скоростью 20 км/ч углубляясь.The 300 hPa chart shows a trough lying North-East to South-West across the track.
– На карте 300 гПа поверхности прослеживается ложбина, пересекая маршрут с северо-востока на юго-запад.The trough is expected to remain in the present position for the next 12 hours.
– Предполагается, что положение ложбины сохранится на ближайшие 12 часов.The semi-permanent high (low) over the Baltic sea is bilding up.
– Квазистационарный антициклон (циклон) формируется над Балтийским морем.Weather along the route (section of the route) will be influenced by... Northern (Southern, Eastern...) periphery of deepening, (filling) cyclone (anticyclone, trough, crest, warm sector of the cyclone).
– Погода по маршруту (участку маршрута) обуславливается... северной (южной, восточной) периферией углубляющегося (заполняющегося) циклона (антициклона, ложбины, гребня, теплым сектором циклона).Weather conditions on the route... to... are therefore expected to be...
– Поэтому по маршруту... ожидаются метеоусловия...Flight in cold (warm, secondary cold, occluded) front zone.
– Полет в зоне холодного (теплого, вторичного холодного, окклюдированного) фронта.Flight along cold (warm...) front (cold front with waves).
– Полет вдоль холодного (теплого) фронта (холодного фронта с волнами).While crossing cold (warm...) front...
– При пересечении холодного (теплого...) фронта...Cold (warm...) front is displacing North (Northeast...) with the speed... kmh, to the East (West...).
– Холодный (теплый...) фронт смещается к северу (северо-востоку...) со скоростью... км/ч, на восток (запад...).An active warm front lying South-East to North-West along the coast of Norway at 12 UTC is moving East at 30 kmh. It is preceded by a narrow belt of heavy snow.
– Активный теплый фронт, пролегающий с юго-востока на северо-запад вдоль побережья Норвегии на 12 UTC, смещается на восток со скоростью 30 км/ч. Ему предшествует узкая зона сильного снегопада.Front is well expressed in temperature contrasts (wind regime, precipitation...).
– Фронт хорошо выражен в температурных контрастах (в ветровом режиме, осадках...).A cold (warm...) front is shown on 12 UTC surface chart.
– На приземной карте, за 12 UTC показан холодный (теплый...) фронт.It is recommended not to cross cold front zone, to go above clouds at a distance not less than 1000 m from CB.
– Рекомендуется не пересекать зону холодного фронта, идти над облаками на расстоянии не менее 1000 м от куч.-дождевых облаков.Warm (high warm) front is placed over Norway at 18 UTC.
– Теплый (высотный теплый) фронт расположен над Норвегией на 18 UTC.In connection with it, it is expected...
– В связи с этим ожидается...Scattered (broken, overcast) clouds (layers), embedded CB
– Рассеянная (значительная, сплошная) облачность (слой), маскированная куч.-дождеваяBase of cloud... km.
– Нижняя граница облачности... км.Top... km.
– Верхняя граница... км.CB top above... km.
– Верхняя границы куч.-дождевой облачности выше... км.Cloud base will be lowering to... m (km) (rapidly). Increasing cloud layers, (local) thunderstorm(s) (probability of thunderstorm, thunderstorm situation is shown on the charts as RISK &)
– Нижняя границы облачности понизится до... м (км) (быстро). Повышающаяся облачность, (местами) гроза(ы), (вероятность грозы, т.е. грозовое положение на картах RISK |^)Cb clouds with tops above 10 km and associated thunderstorms are expected to effect the route
– Предполагается по маршруту влияния куч.-дождевой облачности с верхней границей свыше 10 км и связанные с ней грозы.Light (moderate, severe) icing in cloud (precipitation).
– Слабое (умеренное, сильное) обледенение в облаках (осадках).Moderate (severe) turbulence in cloud (surface layer).
– Умеренная (сильная) турбулентность в облаках (приземном слое).(Orographic) Moderate (severe) clear air turbulence is expected North of... (the jet stream) at... km
– (Орографическая) умеренная (сильная) турбулентность в ясном небе ожидается к северу от... (оси струйного течения) на высоте... кмTo escape icing (turbulence) we advise you to choose flight level over... km.
– Чтобы избежать обледенения (турбулентности) рекомендуем выбрать высоту полета выше... км.Data from boards confirm presence of moderate (severe) icing (turbulence) in cloud.
– Бортовые данные подтверждают наличие умеренного (сильного) обледенения (турбулентности) в облаках.Radar (satellite) data confirm presence of thunderstorms, CB clouds.
– Радиолокационные (спутниковые) данные подтверждают наличие грозовых очагов, куч.-дождевой облачности.Displacing Northward (Southward...).
– Смещение к северу (югу...).Visibility... km (m) (in rain).
– Видимость... км (м) (в дожде). – Улучшение (ухудшение)The altitude of tropopause is... km
– Высота тропопаузы... кмSharp slope of tropopause is observed over area of...
– Резкий наклон тропопаузы наблюдается над районом...Upper wind and temperature, wind and temperature aloft
– Ветер и температура на высотеThe 500 hPa prognostic chart for 12 UTC indicates upper winds of 240 degrees 60 kilometres per hour with temperature minus 20 degrees Celsius
– По 500 гПа прогностической карте за 12 UTC высотный ветер 240° 60 км/ч и температура – 20° СWind direction... degrees (variable)
– Направление ветра... град (неустойчивое)Wind speed... kilometres per hour (metres per second if surface)
– Скорость ветра... км/ч (если приземный – м/сек)Wind speeds over the route Moscow – London are expected to increase (decrease) from... to... kmh
– Предполагается усиление (ослабление) ветра по маршруту Москва – Лондон от... до... км/ч – Изменение ветраIt is expected to remain in the present position for the next 12 hours
– Предполагается сохранение настоящего положения на последующие 12 часов – Максимальный ветерThe jet stream with winds 240 degrees and speed 200 kmh is expected at 12 km
– Струйное течение с ветром 240° 200 км/ч предполагается на высоте 12 км – Борты сообщают о сдвиге ветраAccording data from arriving (departing) aircrafts...
– Согласно данным прибывающих (вылетающих) воздушных судов...Information about observed (expected) existence of wind shear
– Информация о наблюдаемом (ожидаемом) сдвиге ветра(In this case) wind shear conditions are associated with thunderstorm (cold/warm front; strong surface wind; low level temperature inversion)
– (В этом случае) условия сдвига ветра связаны с грозой (холод ным/теплым фронтом; сильным приземным ветром; температурной инверсией в приземном слое)Wind shear could adversly affect aircraft on the takeoff path (in climb out) in layer from runway level to 500 metres
– Сдвиг ветра может оказать неблагоприятное воздействие на воздушное судно на взлете (при наборе высоты) в слое – уровень ВПП/500 м – Интенсивность сдвига ветраWind shear warning surface wind 320/10 wind at 60m 360/25 in approach
– Оповещения о сдвиге ветра – в зоне захода на посадку – приземный ветер 320/10, на высоте 60 м – 360/25B-707 reported moderate (strong, severe) wind shear in approach (while takeoff, in climbout) runway 34 at 15.10
– Б707 сообщает об умеренном (сильном, очень сильном) сдвиге ветра при подходе (на взлете, при наборе высоты) к ВПП 34 в 15.10Temperature between... and (minus)... degrees Celsius
– Температура... (м)... градусов ЦельсияZero isotherm is at the altitude of... km
– Нулевая изотерма на высоте... кмAt the beginning (end, in the middle, in the first half) of the route
– В начале (конце, в середине, в первой половине) маршрутаIt is displacing to the North (South...) Northward (Southward...)
– Смещается к северу (югу...), на север (юг...)Locally from... to...
– Местами от... до...At the altitude of... km
– На высоте... кмIn the layer from (between)... to (and)... km
– В слое... –... км (между)... – При посадке (взлете)The information depicted on high level (wind, temperature) charts should be grid points data
– Информация на высотных картах (ветер, температура) является данными в точках сеткиSatellite nephanalysis for 12 UTC today shows that...
– На основании данных нефанализа за 12 UTC настоящего дня видно, что... – Фактическая погода в пункте вылета (посадки)Runway visual range is... m
– Дальность видимости на ВПП –... мYour alternate is...
– Ваш запасной... – У вас есть вопросы?English-Russian aviation meteorology dictionary > phraseology of meteorological breefing/consultation
-
17 theory
теория; гипотеза
theory of electronegativity мин. теория электроотрицательности
theory of fixation теория фиксации
theory of fractional crystallization теория фракционной кристаллизации
theory of isostasy теория изостазии
theory of radioactivity теория радиоактивности
theory of similarity теория подобия
abyssal theory абиссальная теория (образования месторождений полезных ископаемых)
animal theory теория животного происхождения нефти
antecedent-platform theory теория антецедентной платформы
anticlinal theory of accumulation антиклинальная теория накопления нефти
artesian water circulation theory теория циркуляции артезианских вод
ascension theory теория восходящих (глубинных) растворов
bar theory теория баров (происхождение мощных толщ эвапоритов в лагунах)
capture theory теория захвата
carbon-ratio theory теория углеродного коэффициента
cataclysmic theory теория катаклизм
coal theory теория происхождения нефти из ископаемых углей
communications theory пал. теория связи
compaction theory теория уплотнения
constrained equilibrium theory теория вынужденного равновесия
continental drift theory теория перемещения континентов, теория Вегенера
crust-substratum theory теория субстрата земной коры
curved path theory теория криволинейной траектории
descension theory теория нисходящих (поверхностных) растворов
diastrophic theory of oil accumulation диастрофическая теория нефтенакопления; структурная теория образования залежей нефти
diastrophic theory of oil migration диастрофическая теория миграции нефти
diatom theory теория происхождения нефти из диатомовых водорослей
dilatation theory теория расширения (ледников)
displacement theory теория перемещения континентов, теория Вегенера
dissociation theory теория диссоциации
double-layer theory мин. двухслоевая теория
downbuckling theory уст. гипотеза изгибания складок (симатической коры)
drift theory дрифтовая теория
dynamic theory динамическая теория
dynamo theory теория динамо
elastic rebound theory теория упругого восстановления
equilibrium theory теория равновесия
erupto-tidal theory эруптивно-приливная теория
fissure theory трещинная теория
gas-fluxing' theory теория газового течения
glacial theory ледниковая теория
glacial-control theory теория ледникового контроля (теория образования коралловых атоллов и барьерных рифов)
gravitational theory гравитационная теория (теория миграции нефти и газа)
gravity layered earth theory теория зонального строения земного шара
hydraulic theory гидравлическая теория (теория миграции газа и нефти под влиянием движения подземных вод)
hydrogenation theory теория гидрогенизации (теория органического происхождения нефти)
in situ theory автохтонная теория (образования угля)
isostatic theory изостатическая гипотеза
Jeans and Jeffreys theory приливная теория (происхождения солнечной системы)
Joly's theory теория циклов диастрофизма
land-plant theory теория происхождения нефти из наземных растений
limestone gypsum and hot water theory теория происхождения нефти при воздействии горячей воды на известняк и гипс
magnetohydrodynamics theory магнитогидродинамическая теория
maximum strain theory теория наибольших деформаций
Milankovitch theory астрономическая теория Миланковича
monoglacial theory теория моногляциализма
nappe theory теория шарьяжных покровов, теория тектонических покровов
neptunian theory нептуническая теория (происхождения горных пород)
organic — органическая теория происхождения нефти
oscillation theory осцилляционная теория (связывающая образование главных тектонических структур Земли с космической энергией)
oscillatory-wave theory океаногр. теория колеба тельных волн
peat-to-anthracite theory торфоантрацитовая теория
Pettersson theory теория Петерсона (астрономическая теория изменения климата)
planetesimal theory гипотеза пылевого облака, планетезимальная гипотеза
polyglacial theory теория полигляциализма
progressive-wave theory теория прогрессивных волн
pulsation theory пульсационная гипотеза
regime theory концепция образования русла реки в материале, переносимом и отлагаемом данной рекой
renewal theory теория повторений
replacement theory теория замещения (одна из теорий миграции нефти)
resonating-bond theory теория резонансной связи
sea weed theory теория происхождения нефти из морских водорослей
seepage theory теория фильтрации, теория проса чивания
shrinkage theory теория сжатия, контракционная теория
similitude theory тект. теория подобия
stationary-wave theory океаногр. теория колебательных волн
steady-state theory теория стационарного состояния расширяющейся Вселенной
strain-ellipsoid theory теория эллипсоида деформации, теория эллипсоида напряжения
subsidence theory теория погружения (теория обра зования коралловых атоллов и барьерных рифов)
swamp theory автохтонная теория (образования угля)
syntectic-Iiquation theory синтектически ликвацион ная теория
tabula rasa theory теория «табула раза» (полного уничтожения флоры и фауны во всей Скандинавии под сплошным ледниковым покровом в течение плейстоцена)
tetrahedral theory тетраэдрическая теория (контракции Земли)
thermal contraction theory теория термального сокращения, теория тепловой контракции
tidal theory приливная теория
tidal resonance — теория приливного резонанса
two-magma theory теория двух магм
undation theory теория ундаций (возникновения тектонических структур вследствие восходящих и нисходящих вертикальных движений)
vegetable theory теория растительного происхождения нефти
vitalism theory теория витализма, витализм
Wegener theory теория перемещения континентов, теория Вегенера
Weiss's theory of magnetism теория магнетизма Вейса
zonal theory теория зональности (теория образования гипогенных месторождений полезных ископаемых)
-
18 figure of merit
доброкачественность пьезоэлектрического резонатора
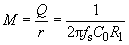
Отношение добротности пьезоэлектрического резонатора к емкостному коэффициенту.
[ ГОСТ 18669-73]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
добротность
1. Количественная характеристика потерь колебательной системы при резонансе, равная
где Wк - полный запас энергии колебаний при резонансе;
Wп - потери энергии за период
[ Физический энциклопедический словарь]
2. Количественная мера потерь колебательной системы. Показывает, во сколько раз амплитуда вынужденных колебаний при резонансе превышает амплитуду на частоте, много меньшей резонансной при одинаковой внешней силе
3. Отношение резонансной частоты спектра колебаний к его ширине на уровне 0,707 от максимального значения амплитуды спектра
Примечание
Определения 2 и 3 являются достаточно точными для систем с высокой добротностью (Q >(5-10)), определение 1 пригодно во всех случаях
[Система неразрушающего контроля. Виды (методы) и технология неразрушающего контроля. Термины и определения (справочное пособие). Москва 2003 г.]
добротность (1)
коэффициент добротности (1)
-
[IEV number 151-15-45]
добротность (2)
коэффициент добротности (2)
-
[IEV number 151-15-46]EN
quality factor (1)
Q factor (1)
for a capacitor or inductor under periodic conditions, ratio of the absolute value of the reactive power to the active power
NOTE 1 – The quality factor is a measure of the losses, usually unwanted, in a capacitor or an inductor.
NOTE 2 – The quality factor depends generally on frequency and voltage.
[IEV number 151-15-45]
quality factor (2)
Q factor (2)
for a resonant circuit at the resonance frequency, 2π times the ratio of the maximum stored energy to the energy dissipated during one period
NOTE – The quality factor is a measure of sharpness of the resonance.
Source: 801-24-12 MOD
[IEV number 151-15-46]FR
facteur de qualité (1), m
facteur de surtension (1), m
pour un condensateur ou une bobine d'inductance en régime périodique, rapport de la valeur absolue de la puissance réactive à la puissance active
NOTE 1 – Le facteur de qualité caractérise les pertes, généralement non désirées, dans un condensateur ou une bobine d'inductance.
NOTE 2 – Le facteur de qualité dépend généralement de la fréquence et de la tension.
[IEV number 151-15-45]
facteur de qualité (2), m
facteur de surtension (2), m
pour un circuit résonant fonctionnant à la fréquence de résonance, 2π fois le rapport de l'énergie maximale emmagasinée dans le circuit à l'énergie dissipée pendant une période
NOTE – Le facteur de qualité caractérise l'acuité de la résonance.
Source: 801-24-12 MOD
[IEV number 151-15-46]Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > figure of merit
-
19 Q factor
добротность
1. Количественная характеристика потерь колебательной системы при резонансе, равная
где Wк - полный запас энергии колебаний при резонансе;
Wп - потери энергии за период
[ Физический энциклопедический словарь]
2. Количественная мера потерь колебательной системы. Показывает, во сколько раз амплитуда вынужденных колебаний при резонансе превышает амплитуду на частоте, много меньшей резонансной при одинаковой внешней силе
3. Отношение резонансной частоты спектра колебаний к его ширине на уровне 0,707 от максимального значения амплитуды спектра
Примечание
Определения 2 и 3 являются достаточно точными для систем с высокой добротностью (Q >(5-10)), определение 1 пригодно во всех случаях
[Система неразрушающего контроля. Виды (методы) и технология неразрушающего контроля. Термины и определения (справочное пособие). Москва 2003 г.]
добротность (1)
коэффициент добротности (1)
-
[IEV number 151-15-45]
добротность (2)
коэффициент добротности (2)
-
[IEV number 151-15-46]EN
quality factor (1)
Q factor (1)
for a capacitor or inductor under periodic conditions, ratio of the absolute value of the reactive power to the active power
NOTE 1 – The quality factor is a measure of the losses, usually unwanted, in a capacitor or an inductor.
NOTE 2 – The quality factor depends generally on frequency and voltage.
[IEV number 151-15-45]
quality factor (2)
Q factor (2)
for a resonant circuit at the resonance frequency, 2π times the ratio of the maximum stored energy to the energy dissipated during one period
NOTE – The quality factor is a measure of sharpness of the resonance.
Source: 801-24-12 MOD
[IEV number 151-15-46]FR
facteur de qualité (1), m
facteur de surtension (1), m
pour un condensateur ou une bobine d'inductance en régime périodique, rapport de la valeur absolue de la puissance réactive à la puissance active
NOTE 1 – Le facteur de qualité caractérise les pertes, généralement non désirées, dans un condensateur ou une bobine d'inductance.
NOTE 2 – Le facteur de qualité dépend généralement de la fréquence et de la tension.
[IEV number 151-15-45]
facteur de qualité (2), m
facteur de surtension (2), m
pour un circuit résonant fonctionnant à la fréquence de résonance, 2π fois le rapport de l'énergie maximale emmagasinée dans le circuit à l'énergie dissipée pendant une période
NOTE – Le facteur de qualité caractérise l'acuité de la résonance.
Source: 801-24-12 MOD
[IEV number 151-15-46]Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
коэффициент Q
Результат измерения качества принятого сигнала (МСЭ-Т G.972).
[ http://www.iks-media.ru/glossary/index.html?glossid=2400324]Тематики
- электросвязь, основные понятия
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Q factor
-
20 QF
- форма отчётности по качеству
- тепловое напряжение сечения камеры сгорания
- зарегистрированные энергетические мощности, не входящие в энергокомпании
- добротность
добротность
1. Количественная характеристика потерь колебательной системы при резонансе, равная
где Wк - полный запас энергии колебаний при резонансе;
Wп - потери энергии за период
[ Физический энциклопедический словарь]
2. Количественная мера потерь колебательной системы. Показывает, во сколько раз амплитуда вынужденных колебаний при резонансе превышает амплитуду на частоте, много меньшей резонансной при одинаковой внешней силе
3. Отношение резонансной частоты спектра колебаний к его ширине на уровне 0,707 от максимального значения амплитуды спектра
Примечание
Определения 2 и 3 являются достаточно точными для систем с высокой добротностью (Q >(5-10)), определение 1 пригодно во всех случаях
[Система неразрушающего контроля. Виды (методы) и технология неразрушающего контроля. Термины и определения (справочное пособие). Москва 2003 г.]
добротность (1)
коэффициент добротности (1)
-
[IEV number 151-15-45]
добротность (2)
коэффициент добротности (2)
-
[IEV number 151-15-46]EN
quality factor (1)
Q factor (1)
for a capacitor or inductor under periodic conditions, ratio of the absolute value of the reactive power to the active power
NOTE 1 – The quality factor is a measure of the losses, usually unwanted, in a capacitor or an inductor.
NOTE 2 – The quality factor depends generally on frequency and voltage.
[IEV number 151-15-45]
quality factor (2)
Q factor (2)
for a resonant circuit at the resonance frequency, 2π times the ratio of the maximum stored energy to the energy dissipated during one period
NOTE – The quality factor is a measure of sharpness of the resonance.
Source: 801-24-12 MOD
[IEV number 151-15-46]FR
facteur de qualité (1), m
facteur de surtension (1), m
pour un condensateur ou une bobine d'inductance en régime périodique, rapport de la valeur absolue de la puissance réactive à la puissance active
NOTE 1 – Le facteur de qualité caractérise les pertes, généralement non désirées, dans un condensateur ou une bobine d'inductance.
NOTE 2 – Le facteur de qualité dépend généralement de la fréquence et de la tension.
[IEV number 151-15-45]
facteur de qualité (2), m
facteur de surtension (2), m
pour un circuit résonant fonctionnant à la fréquence de résonance, 2π fois le rapport de l'énergie maximale emmagasinée dans le circuit à l'énergie dissipée pendant une période
NOTE – Le facteur de qualité caractérise l'acuité de la résonance.
Source: 801-24-12 MOD
[IEV number 151-15-46]Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
зарегистрированные энергетические мощности, не входящие в энергокомпании
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
тепловое напряжение сечения камеры сгорания
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
форма отчётности по качеству
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > QF
- 1
- 2
См. также в других словарях:
maximum — [ maksimɔm ] n. m. • 1718; mot lat. « le plus grand » 1 ♦ Math. Valeur d une fonction supérieure à celles qui la précèdent ou la suivent immédiatement. Premier, second maximum d une fonction, d une courbe, d un graphique. ⇒ pointe. 2 ♦ (1751)… … Encyclopédie Universelle
Regime de retraite des artisans francais — Régime de retraite des artisans français Le régime de retraite des artisans est rattaché depuis le 1er juillet 2006 au Régime social des indépendants (RSI). Création en 1948 du régime d assurance vieillesse des artisans (AVA) géré par la Caisse… … Wikipédia en Français
Regime de retraite des commercants francais — Régime de retraite des commerçants français Le régime de retraite des commerçants français est un régime français concernant les travailleurs indépendants du commerce, de l industrie et des services et les entreprises de plus de 10 salariés… … Wikipédia en Français
régime — 1. régime [ reʒim ] n. m. • 1408; regisme « royaume » 1190; lat. regimen « action de diriger » → régir 1 ♦ Vx Façon d administrer, de gouverner une communauté. Par ext. (1789) Mod. Organisation politique, économique, sociale d un État. ⇒ système … Encyclopédie Universelle
Maximum sustainable yield — In population ecology and economics, maximum sustainable yield or MSY is, theoretically, the largest yield (or catch) that can be taken from a species stock over an indefinite period. Fundamental to the notion of sustainable harvest, the concept… … Wikipedia
Régime de Vichy — Pour les articles homonymes, voir Vichy (homonymie) et État français (homonymie). État français Régime de Vichy … Wikipédia en Français
Régime spécial de retraites — Régimes spéciaux de retraite En France, les régimes spéciaux de retraite sont des régimes de retraite dont bénéficient des employés de certaines grandes entreprises publiques, (SNCF, RATP), ou de branches entières comme celle des Industries… … Wikipédia en Français
Régime spécial des retraites — Régimes spéciaux de retraite En France, les régimes spéciaux de retraite sont des régimes de retraite dont bénéficient des employés de certaines grandes entreprises publiques, (SNCF, RATP), ou de branches entières comme celle des Industries… … Wikipédia en Français
Régime Dukan — Le régime Dukan (aussi appelé régime Protal pour protéine et alternance) est un régime amaigrissant mis au point par le docteur Pierre Dukan[1]. Sommaire 1 Principe 2 Efficacité … Wikipédia en Français
Régime enregistré d'épargne-études — Le régime enregistré d épargne études (REEE) permet aux épargnes pour les études de croître à l abri de l impôt dans un régime d épargne spécial enregistré par le Gouvernement du Canada jusqu à ce que l enfant nommé dans le REEE s inscrive à un… … Wikipédia en Français
Régime de neutre — Schéma de liaison à la terre Pour les articles homonymes, voir SLT. En électricité, un Schéma de Liaison à la Terre, ou SLT (Anciennement Régime de neutre) définit le mode de raccordement à la terre du point neutre d un transformateur de… … Wikipédia en Français